|
Filtration in Bottled Water Processing Despite controversy over the health benefits of bottled water versus that from municipal water supplies and home drinking water filtration systems, bottled water represents one of the fastest growing segments of the beverage industry with an annual growth rate of well over 10%. Much of the growth is fueled by consumers choosing bottled water over soda and public concerns over drinking water safety. Bottled water is an excellent consumer beverage because of its consistent safety, quality, good taste and convenience. Bottled water is regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and is also subject to additional regulations. There are several categories of bottled water, including: Spring Water – Derived from an underground formation from which water flows naturally to the surface of the earth, spring water must be collected only at the spring or through a borehole tapping the underground formation feeding the spring. Purified Water – Produced by distillation, deionization, reverse osmosis or other processes, purified water is sometimes labeled with its production method, such as distilled water or deionized water. Mineral Water – Containing at least 250 parts per million total dissolved solids, mineral water is distinguished from other types of bottled water by its constant level and relative proportions of mineral and trace elements at the point of emergence from the source. No minerals can be added to this product.
|
Sparkling Bottled Water – With the same amount of carbon dioxide that it had when obtained from the source (following treatment and possible replacement of carbon dioxide), sparkling bottled waters may be labeled as “sparkling drinking water,” “sparkling mineral water,” “sparkling spring water,” etc. Artesian Water/Artesian Well Water – A well that taps a confined aquifer (a water-bearing underground layer of rock or sand) is the source for this water. The source water level stands at some height above the top of the aquifer. Well Water – A water aquifer is simply tapped with a bored/tapper hole to obtain well water.
|
|
Traditional Water Filtration Methods 1. Boiling Historically, boiling is what has been used to disinfect water from microorganisms. In fact, when done correctly, it can kill most bacteria, but not all. Bacteria and protozoa are killed at the first bubble, and it takes about three minutes to kill the rest. The drawbacks to this filtration method:
Boiling water may be the only method during situations like camping, but in a household, there are more effective and efficient methods available. 2. Chemical There are two primary chemicals used to purify water: iodine and chlorine. Both are lightweight, low cost and easy to use. Iodine has been proven effective in killing off viruses, bacteria and protozoa. However, the colder the water is, the more time it will take to purify with iodine. Iodine can also absorb into the dirt and debris naturally found in water, so the dosage will always vary. Also, pregnant women or those with thyroid conditions should not drink water with the chemical. Usually, iodine is just used for short-term purposes, and should not be used for more than three consecutive months. Many do not favor the taste it leaves behind either. The unfavorable taste can be combated by mixing the water with a sugar-based drink mix, or better yet, by not using the method at all. Chlorine bleach is the second chemical purifier. The process of chlorination will cause dirt and debris to settle to the bottom of the water container and make the water visually clearer. The American Red Cross endorses the brand Chlorox. The Red Cross states that people should use an unscented household bleach that contains 5.25% sodium hypochlorite. When using |
bleach to purify, the recommendation is to add 16 drops of bleach per gallon of water, stir, and let stand for 30 minutes. If the water does not have a slight bleach odor, repeat the dosage and let stand another 15 minutes. There are many drawbacks to the chlorination method. If the household bleach is over six months old, it may not have enough potency to disinfect. Also, chlorine is very poisonous and adding too much can cause illness, internal organ damage or even death. Chlorine has been linked to many health problems. You can read about them in the health section of this site. Also, if one decides to use bleach, be sure to add it at the time intended to use the water, not when storing. Seeing the drawbacks of these traditional filtration methods brings us to understand why more advanced water purification are required nowadays. Advanced Modern Water Purification Methods Water filtration by definition simply means to strain out the impurities from a water source. The larger the impurity particulate, the easier it is to filter. The opposite is true: the smaller the impurity particulate, the harder it is to remove. Thus, the size of the filter pore and the durability of the filtering element are important to the filter's longevity and its ability to perform. Most filtering elements are made of ceramic, glass fiber, hard-block carbon, or materials that resemble compressed surgical paper. Some of the better purification methods include the activated carbon and reverse osmosis. The best contribution that carbon makes to filtration technology is its ability to reduce chemical quantities, poor taste, odors and many pollutants. Because carbon is only mildly effective in filtering out particulates and microorganisms, it is mostly used as a second or third stage filter in home and portable water use. It is seldom used as a stand-alone filtering, and often times, used in conjunction with reverse osmosis. Reverse osmosis, which uses a semipermable membrane filter to separate the water from contaminants. Reverse osmosis is highly effective in removing several impurities from water such as total dissolved solids, turbidity, asbestos, lead and other toxic heavy metals, radium, and many dissolved organic. The process will also remove chlorine, and can also remove nuclear radiation such as radioactive plutonium or strontium in the drinking water. Therefore, reverse osmosis combined with activated carbon seems to be the most advanced water purification method developed so far. Refrences : http://www.freedrinkingwater.com |
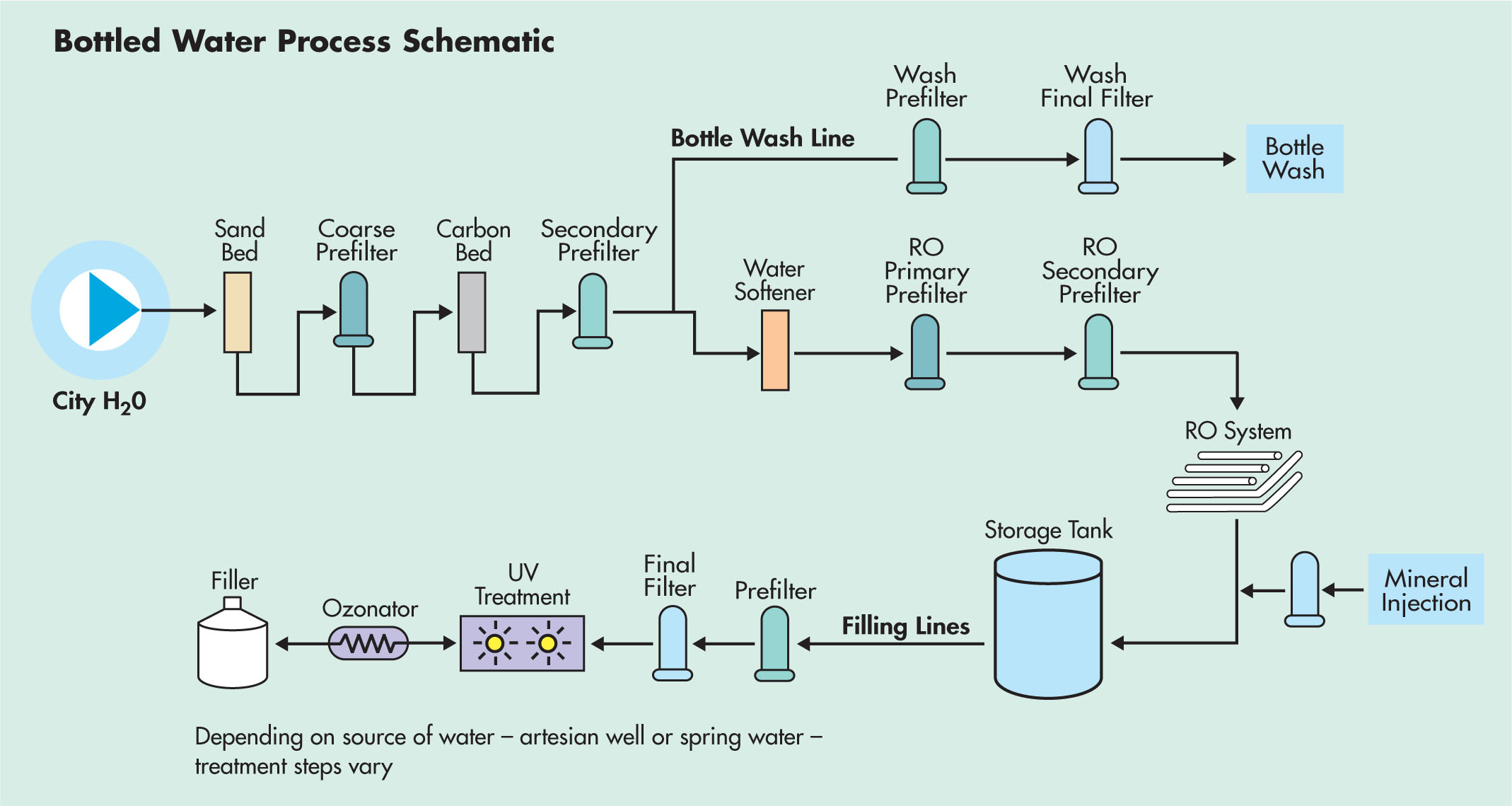
|
The Role of Filtration Effective filtration systems remove 100% of undesirable contaminants and microbial content. With its broad line of polypropylene and microfiberglass prefilters, Graver offers cost effective filtration regardless of incoming water quality.
Cryptosporidium is an emerging health threat in water and Cryptosporidiosis is fatal in immune deficient persons. Cryptosporidium is difficult to remove from water because it is resistant to chlorination. Though Bottled Water is regulated in the United States by FDA, presently there are no standards for Cryptosporidium in Bottled Water and regulation is by voluntary conformance. For final filtration, the QCR™ Cyst Reduction filter is designed to exceed the ANSI/NSF Standard 53 for the removal of Crytosporidium oocyst and Giardia lamblia cysts.
Or if bacterial contaminants are of concern, the ZTEC-B polyethersulfone membrane cartridge has been validated for the removal of numerous ATCC species. When it comes to producing bottled water, nothing builds success like consistently high quality. Graver Technologies filtration expertise provides bottled water manufacturers with consistency in taste and color, coupled with superior filtration system performance.
|
Contact US NOW!!! FOR THE BEST WATER FILTRATION AND PURIFICATION SOLUTION!!!!!!
|



